It is one of the most widely known modeling technique. In this technique, the dependent variable is continuous, independent variable(s) can be continuous or discrete, and nature of regression line is linear.
Linear Regression establishes a relationship between dependent variable (Y) and one or more independent variables (X) using a best fit straight line (also known as regression line).
Linear regression can be implemented by varius techniques , but it can be visualized by tensorflow in a very different way.
#Import Libraies import tensorflow as tf import numpy import matplotlib.pyplot as plt rng = numpy.random # Parameters learning_rate = 0.01 training_epochs = 1000 display_step = 50 # Training Data train_X = numpy.asarray([3.3,4.4,5.5,6.71,6.93,4.168,9.779,6.182,7.59,2.167, 7.042,10.791,5.313,7.997,5.654,9.27,3.1]) train_Y = numpy.asarray([1.7,2.76,2.09,3.19,1.694,1.573,3.366,2.596,2.53,1.221, 2.827,3.465,1.65,2.904,2.42,2.94,1.3]) n_samples = train_X.shape[0]
# tf Graph Input
X = tf.placeholder('float')
Y = tf.placeholder('float')
# Set model weights
W = tf.Variable(rng.randn(), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(rng.randn(), name='bias')
# Construct a linear model
pred = tf.add(tf.multiply(X, W), b)# Mean squared error cost = tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(pred-Y, 2))/(2*n_samples) # Gradient descent optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# Initializing the variables init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for (x, y) in zip(train_X, train_Y):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y})
# Display logs per epoch step
if (epoch+1) % display_step == 0:
c = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y:train_Y})
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(c), \
"W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b))
print("Optimization Finished!")
training_cost = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: train_X, Y: train_Y})
print("Training cost=", training_cost, "W=", sess.run(W), "b=", sess.run(b), '\n')
# Graphic display
plt.plot(train_X, train_Y, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.plot(train_X, sess.run(W) * train_X + sess.run(b), label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Testing example, as requested (Issue #2)
test_X = numpy.asarray([6.83, 4.668, 8.9, 7.91, 5.7, 8.7, 3.1, 2.1])
test_Y = numpy.asarray([1.84, 2.273, 3.2, 2.831, 2.92, 3.24, 1.35, 1.03])
print("Testing... (Mean square loss Comparison)")
testing_cost = sess.run(
tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(pred - Y, 2)) / (2 * test_X.shape[0]),
feed_dict={X: test_X, Y: test_Y}) # same function as cost above
print("Testing cost=", testing_cost)
print("Absolute mean square loss difference:", abs(training_cost - testing_cost))
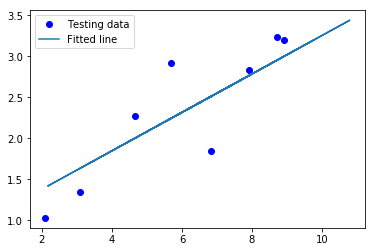
plt.plot(test_X, test_Y, 'bo', label='Testing data')
plt.plot(train_X, sess.run(W) * train_X + sess.run(b), label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
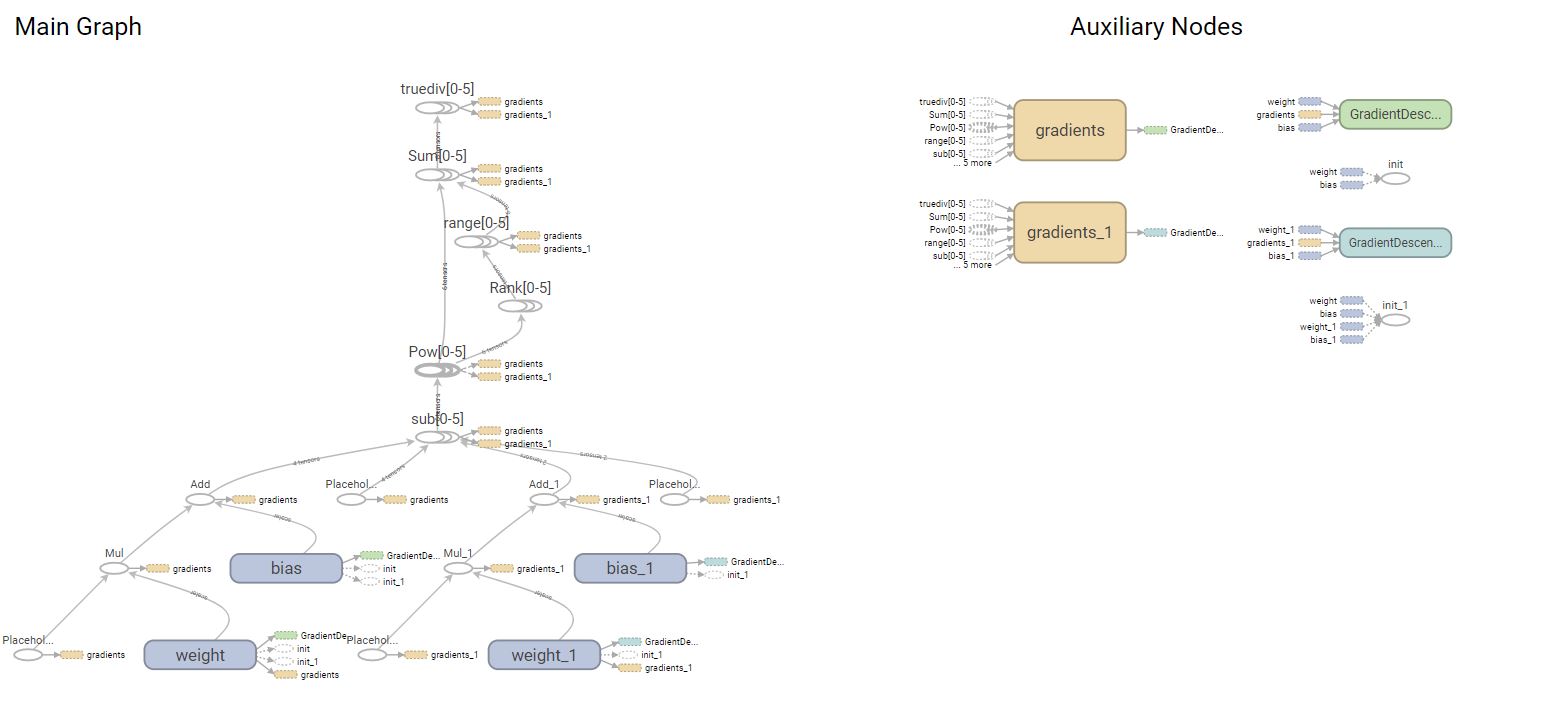
writer= tf.summary.FileWriter('D:\Graph\Tensorflow',sess.graph)
writer.close()
sess.close()
Output:
Epoch: 0050 cost= 0.084654316 W= 0.200937 b= 1.1515 Epoch: 0100 cost= 0.083774000 W= 0.203831 b= 1.13068 Epoch: 0150 cost= 0.082994938 W= 0.206553 b= 1.1111 Epoch: 0200 cost= 0.082305610 W= 0.209113 b= 1.09268 Epoch: 0250 cost= 0.081695616 W= 0.21152 b= 1.07537 Epoch: 0300 cost= 0.081155792 W= 0.213784 b= 1.05908 Epoch: 0350 cost= 0.080678098 W= 0.215914 b= 1.04375 Epoch: 0400 cost= 0.080255359 W= 0.217917 b= 1.02935 Epoch: 0450 cost= 0.079881236 W= 0.219801 b= 1.01579 Epoch: 0500 cost= 0.079550095 W= 0.221573 b= 1.00304 Epoch: 0550 cost= 0.079257071 W= 0.223239 b= 0.991056 Epoch: 0600 cost= 0.078997687 W= 0.224807 b= 0.979779 Epoch: 0650 cost= 0.078768112 W= 0.226281 b= 0.969173 Epoch: 0700 cost= 0.078564890 W= 0.227668 b= 0.959197 Epoch: 0750 cost= 0.078385077 W= 0.228972 b= 0.949818 Epoch: 0800 cost= 0.078225911 W= 0.230198 b= 0.940996 Epoch: 0850 cost= 0.078085005 W= 0.231351 b= 0.932699 Epoch: 0900 cost= 0.077960268 W= 0.232436 b= 0.924895 Epoch: 0950 cost= 0.077849805 W= 0.233457 b= 0.917556 Epoch: 1000 cost= 0.077752024 W= 0.234416 b= 0.910652 Optimization Finished! Training cost= 0.077752 W= 0.234416 b= 0.910652

Testing... (Mean square loss Comparison) Testing cost= 0.0829709 Absolute mean square loss difference: 0.00521892
After running the code if you need to visualize the graph use the below code:
In order to run Tensorboard:
In ubuntu we can use:
tensorboard --logdir=/home/user/graph/
In Windows we have to change the command prompt to the directory in which the graph file is placed and then use:
tensorboard --logdir=\home\user\graph\
On the command prompt, we type the below code:
(tensorflowcpu) D:\Graph\Tensorflow>tensorboard --logdir \D:\Graph\Tensorflow\ TensorBoard 0.4.0rc3 at http://y700Vivek:6006 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Nice article!
It’s very useful